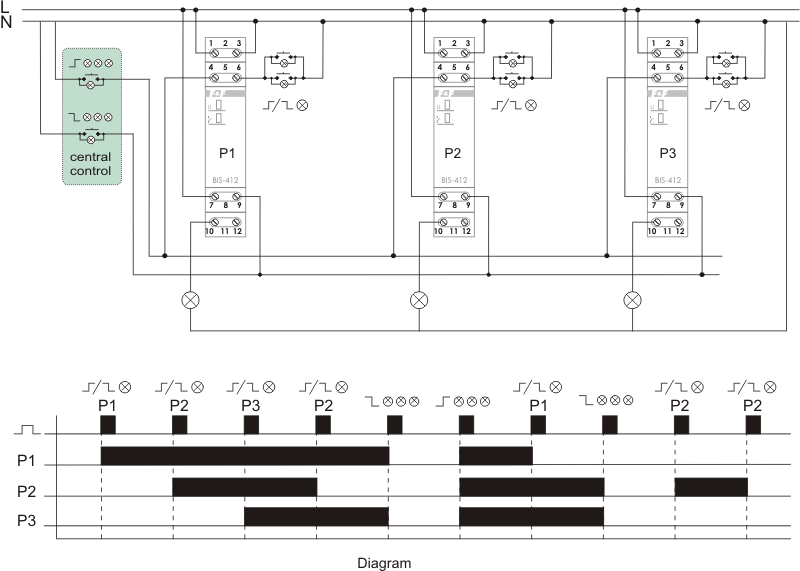
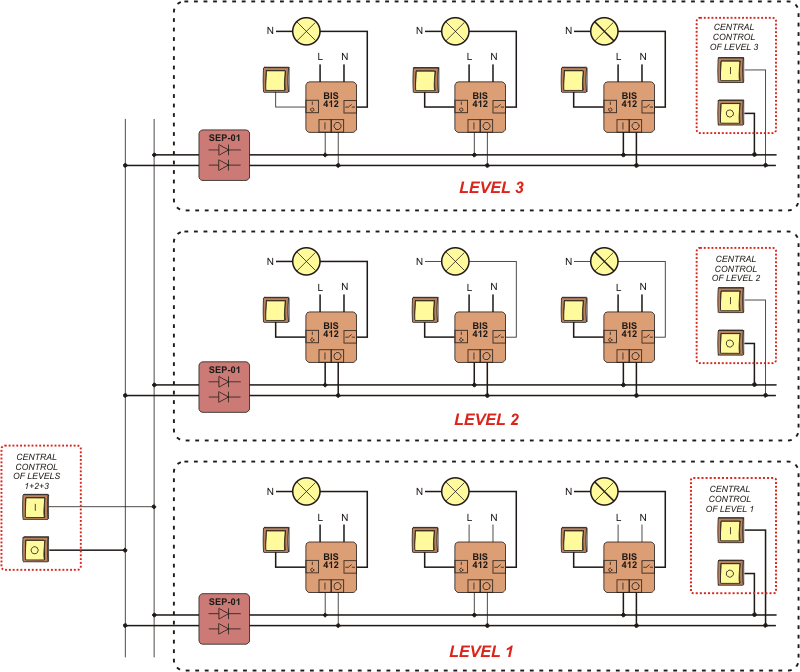
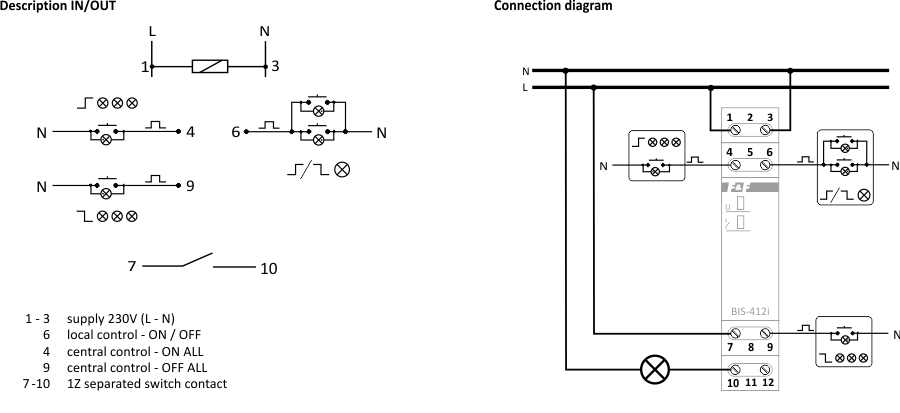
A single relay enables the activation and deactivation of the receiver controlled after each current pulse triggered by pushing a local control momentary push-button (bell-push). The group configuration enables the deactivation or activation of all receivers connected to individual relays by means of the central control push-buttons.
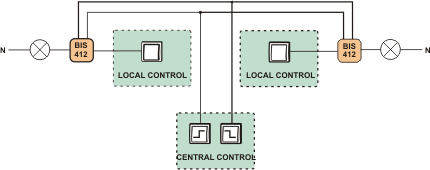
Functioning:
Local control
The receiver is activated after a current pulse that is triggered by pushing one optional momentary push-button ![]() belonging to the local control group. The contact of the relay is switched to the 7-10 position. After a next current pulse, the receiver will be deactivated (the contact of the relay returns to the 7-12 position).
belonging to the local control group. The contact of the relay is switched to the 7-10 position. After a next current pulse, the receiver will be deactivated (the contact of the relay returns to the 7-12 position).
Central control
DEACTIVATE ALL – after a current pulse triggered by pushing the momentary push-button ![]() , all receivers will be deactivated (regardless of their status, i.e. deactivation or activation) that are controlled separately by individual relays. The contact in each relay will be switched to the 7-12 position.
, all receivers will be deactivated (regardless of their status, i.e. deactivation or activation) that are controlled separately by individual relays. The contact in each relay will be switched to the 7-12 position.
ACTIVATE ALL – after a current pulse triggered by pushing the momentary push-button ![]() , all receivers will be activated (regardless of their status, i.e. deactivation or activation) that are controlled separately by individual relays. The contact in each relay will be switched to the 7-10 position.
, all receivers will be activated (regardless of their status, i.e. deactivation or activation) that are controlled separately by individual relays. The contact in each relay will be switched to the 7-10 position.
Attention!
The BIS-412i 230V is compatible with bell pushes equipped with fluorescent lamps. ![]()
Tips
Illuminated buttons
Due to the low supply voltage, illuminated buttons should not be used. Maximum load current The contact current given in the technical data is the maximum value and may be subject to restrictions – more information. If the information provided indicates that the relay in the device is insufficient, it is recommended to use an external switching element (e.g. contactor) adapted to switch large surge currents. State memory The relay does not have a “memory” of the contact position. This means that after the power supply is switched on, the relay contact will always remain in the off state. Resistance to surge currents The device uses an “inrush” type relay characterized by high resistance to short-term surge currents generated, for example, when switching on LED lamps, ESL fluorescent lamps, electronic transformers, discharge lamps, etc.